本文所分析代码版本为spring boot/cloud 2.2.6。
预备知识
一些注解的说明
eureka中用到几个比较有意思的注解,简化程序实现。
@ConfigurationProperties(“eureka.instance”)
表示从外部配置文件中(properties或是yml文件)读取”eureka.instance”对应的配置。
@ConditionalOnBean/@ConditionalOnClass
@ConditionalOnBean // 当给定的在bean存在时,则实例化当前Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean // 当给定的在bean不存在时,则实例化当前Bean @ConditionalOnClass // 当给定的类名在类路径上存在,则实例化当前Bean @ConditionalOnMissingClass // 当给定的类名在类路径上不存在,则实例化当前Bean
可以参考这篇文章:
比如EurekaClientAutoConfiguration类定义中,类上面注解了@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class),表示当在类路径中存在EurekaClientConfig.class,则实例化当前EurekaClientAutoConfiguration。
@ImplementedBy
google guice注解,指定接口默认的实现类。
@Singleton
jdk 提供的注解,将当前类实现为单例模式。
eureka架构
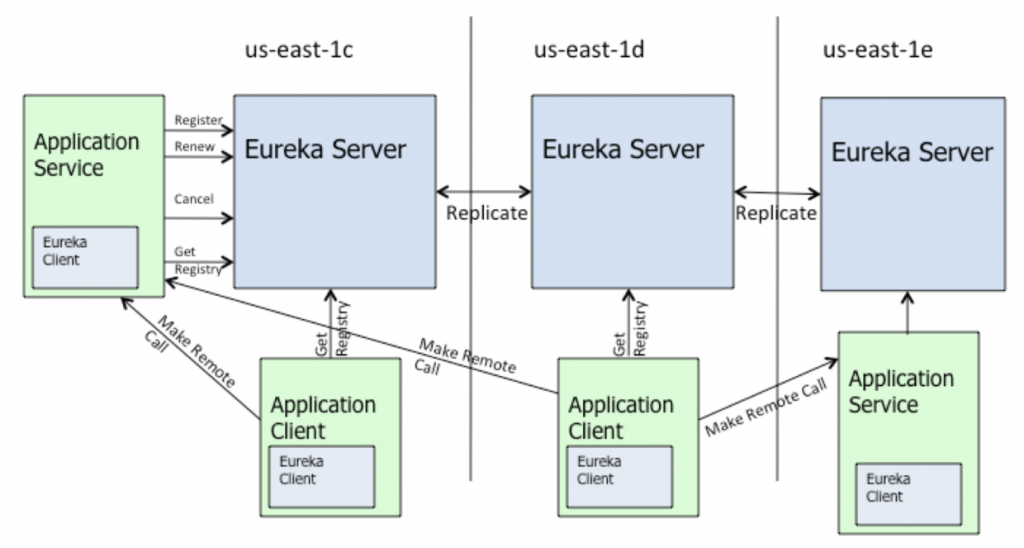
eureka客户端源码
eureka客户端工作流程
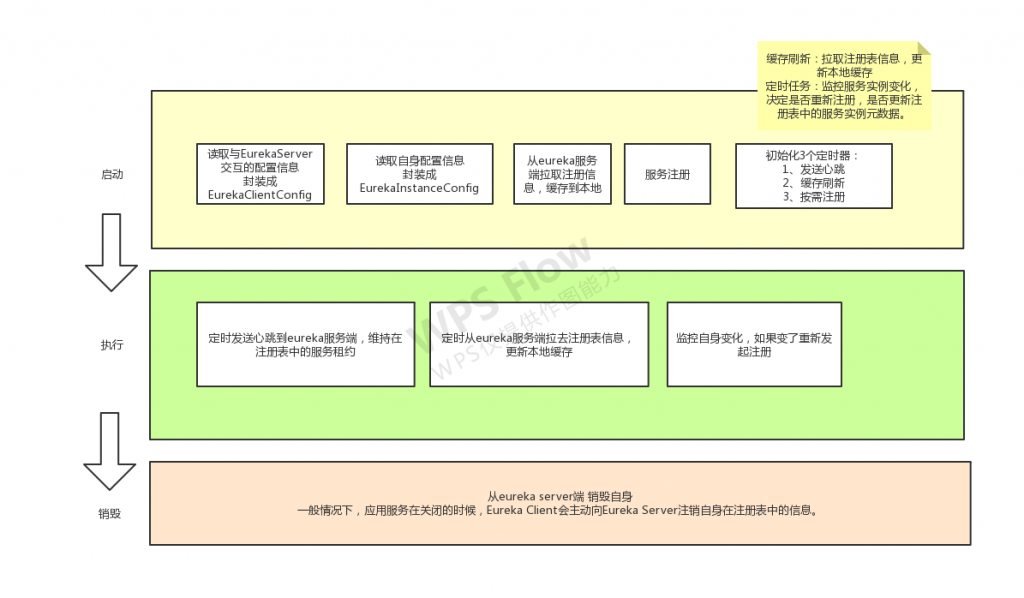
下面将简要说明上图的过程。
eureka客户端比较关键的类如下:
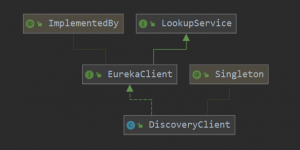
其中,DiscoveryClient是核心,它实现了EurekaClient接口,是该接口的默认实现(@ImplementedBy传入的是DiscoveryClient.class)。另外,@Singleton注解声明了DiscoveryClient是单例。
DiscoverClient
该类的关键方法如下:
//服务注册相关 boolean register() void unregister() //服务续约 boolean renew() //关闭eureka client public synchronized void shutdown() //检查当前client状态,当client状态发生变化时,将会触发新的注册事件,去更新eureka server的注册表中的服务实例信息。 public void registerHealthCheck(HealthCheckHandler healthCheckHandler) //注册事件监听器,当实例信息有变时,触发对应的处理事件。 public void registerEventListener(EurekaEventListener eventListener)
其构造方法DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider, EndpointRandomizer endpointRandomizer)中,此方法中依次执行了 从eureka server中拉取注册表,服务注册,初始化发送心跳,缓存刷新(定时拉取注册表信息),按需注册定时任务等,贯穿了Eureka Client启动阶段的各项工作。
此处给出一些简单的分析:
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider, EndpointRandomizer endpointRandomizer) {
......
//shouldFetchRegistry,其实现类为EurekaClientConfigBean,找到它其实对应于:eureka.client.fetch-register,true:表示client从server拉取注册表信息。
if (config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRY_PREFIX + "lastUpdateSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
}
//shouldRegisterWithEureka,点其实现类EurekaClientConfigBean,找到它其实对应于:eureka.client.register-with-eureka:true:表示client将注册到server。
if (config.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRATION_PREFIX + "lastHeartbeatSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
}
......
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
//用于发送心跳
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
//用于刷新缓存
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
//eurekaTransport是eureka Client和eureka server进行http交互jersey客户端。点开EurekaTransport,看到许多httpclient相关的属性。
eurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport();
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
....
//从eureka server拉取注册表中的信息,将注册表缓存到本地,可以就近获取其他服务信息,减少于server的交互。
boolean primaryFetchRegistryResult = fetchRegistry(false);
......
}
//register()进行注册,若注册失败则抛出异常
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && clientConfig.shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit()) {
try {
if (!register() ) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Registration error at startup. Invalid server response.");
}
} catch (Throwable th) {
logger.error("Registration error at startup: {}", th.getMessage());
throw new IllegalStateException(th);
}
}
//启动调度任务
initScheduledTasks();
}
DiscoveryClient构造方法小结
构造方法中主要进行如下工作:
-
初始化各种信息
-
从eureka server拉取注册表信息
-
向server注册自己
-
初始化3个任务
以下对重要过程进行分析:
拉取注册表过程
对应private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch)方法,参考注释、源码可以知道逻辑如下:
如果增量式拉取被禁止或第一次拉取注册表,则进行全量拉取:getAndStoreFullRegistry()。 否则进行增量拉取注册表信息getAndUpdateDelta(applications)。 一般情况,在Eureka client第一次启动,会进行全量拉取。之后的拉取都尽量尝试只进行增量拉取。 拉取服务注册表: 全量拉取:getAndStoreFullRegistry(); 增量拉取:getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
全量拉取 getAndStoreFullRegistry()
进入getAndStoreFullRegistry() 方法,有一方法:eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications。 通过debug发现 实现类是AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient,点开,debug出 webResource地址为:http://root:root@eureka-7900:7900/eureka/apps/,此端点用于获取server中所有的注册表信息。 getAndStoreFullRegistry()可能被多个线程同时调用,导致新拉取的注册表被旧的覆盖(如果新拉取的动作设置apps阻塞的情况下)。 此时用了AutomicLong来进行版本管理,如果更新时版本不一致,不保存apps。 通过这个判断fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1),如果版本一致,并设置新版本(+1), 接着执行localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));过滤并洗牌apps。点开this.filterAndShuffle(apps)实现,继续点apps.shuffleAndIndexInstances,继续点shuffleInstances,继续点application.shuffleAndStoreInstances,继续点_shuffleAndStoreInstances,发现if (filterUpInstances && InstanceStatus.UP != instanceInfo.getStatus())。只保留状态为UP的服务。
增量拉取getAndUpdateDelta(applications)
回到刚才的fetchRegistry方法中,getAndUpdateDelta,增量拉取。通过getDelta方法,看到实际拉取的地址是:apps/delta,如果获取到的delta为空,则全量拉取。 通常来讲是3分钟之内注册表的信息变化(在server端判断),获取到delta后,会更新本地注册表。 增量式拉取是为了维护client和server端 注册表的一致性,防止本地数据过久,而失效,采用增量式拉取的方式,减少了client和server的通信量。 client有一个注册表缓存刷新定时器,专门负责维护两者之间的信息同步,但是当增量出现意外时,定时器将执行,全量拉取以更新本地缓存信息。更新本地注册表方法updateDelta,有一个细节。 if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) ,public enum ActionType { ADDED, // Added in the discovery server MODIFIED, // Changed in the discovery server DELETED // Deleted from the discovery server }, 在InstanceInfo instance中有一个instance.getActionType(),ADDED和MODIFIED状态的将更新本地注册表applications.addApplication,DELETED将从本地剔除掉existingApp.removeInstance(instance)。
服务注册过程
DiscoveryClient构造函数中,拉取fetchRegistry完后进行register注册。由于构造函数开始时已经将服务实例元数据封装好了instanceInfo,所以此处之间向server发送instanceInfo, 通过方法httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);看到String urlPath = "apps/" + info.getAppName();又是一个server端点,退上去f7,httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NO_CONTENT.getStatusCode();204状态码,则注册成功。
初始化3个定时任务
有3个:
-
心跳定时任务:client会定时向server发送心跳,维持自己服务租约的有效性,用心跳定时任务实现;
-
缓存定时任务:server中会有不同的服务实例注册或是下线,所以client需要定时从server拉取注册表信息,用缓存定时任务实现。
-
按需注册的定时任务,当instanceinfo和status发生变化时,需要向server同步,去更新自己在server中的实例信息。保证server注册表中服务实例信息的有效和可用。
参见initScheduledTasks()。
心跳定时任务和缓存刷新定时任务是有scheduler 的 schedule提交的,查看scheduler变量声明上,看到注释:
A scheduler to be used for the following 3 tasks: - updating service urls - scheduling a TimedSuperVisorTask。
由此可以知道循环逻辑是由TimedSuperVisorTask实现的。
//心跳定时任务
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread())
//HeartbeatThread线程内部run方法定义如下:
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable{
public void run() {
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
//缓存定时任务
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
//CacheRefreshThread线程内部run方法定义如下:
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
refreshRegistry();
}
}
//还有一个定时任务,按需注册。当instanceinfo和status发生变化时,需要向server同步,去更新自己在server中的实例信息。保证server注册表中服务实例信息的有效和可用。
// InstanceInfo replicator
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize
statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
public String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";
}
public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||
InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involved
logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();
}
};
if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
//此定时任务有2个部分,
// 1:定时刷新服务实例信息和检查应用状态的变化,在服务实例信息发生改变的情况下向server重新发起注册。InstanceInfoReplicator点进去。看到一个方法
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();//刷新instanceinfo。
//如果实例信息有变,返回数据更新时间。
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
discoveryClient.register();//注册服务实例。
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
//延时执行下一个检查任务。用于再次调用run方法,继续检查服务实例信息和状态的变化。
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
refreshInstanceInfo点进去,看方法注释:如果有变化,在下次心跳时,同步向server。
//2.注册状态改变监听器,在应用状态发生变化时,刷新服务实例信息,在服务实例信息发生改变时向server注册。 看这段
statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
public String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";
}
public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||
InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involved
logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();
}
};如果状态发生改变,调用onDemandUpdate(),点onDemandUpdate进去,看到InstanceInfoReplicator.this.run();
//总结:两部分,一部分自己去检查,一部分等待状态监听事件。
//初始化定时任务完成,最后一步启动步骤完成。接下来就是正常服务于业务。然后消亡。
服务下线
服务下线:在应用关闭时,client会向server注销自己,在Discoveryclient销毁前,会执行下面清理方法。
//此方法上有一个注解,表示:在销毁前执行此方法。unregisterStatusChangeListener注销监听器。
public synchronized void shutdown() {
......
//取消定时任务。
cancelScheduledTasks();
......
//服务下线。
unregister();
//关闭jersy客户端
eurekaTransport.shutdown();
//其他操作
......
}
unregister点进去。cancel点进去。AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient。String urlPath = "apps/" + appName + '/' + id;看到url和http请求delete方法。
更多
更进一步的启动流程分析,可以参考这篇文章:
下面这张图即来自该文章,感觉还可以。
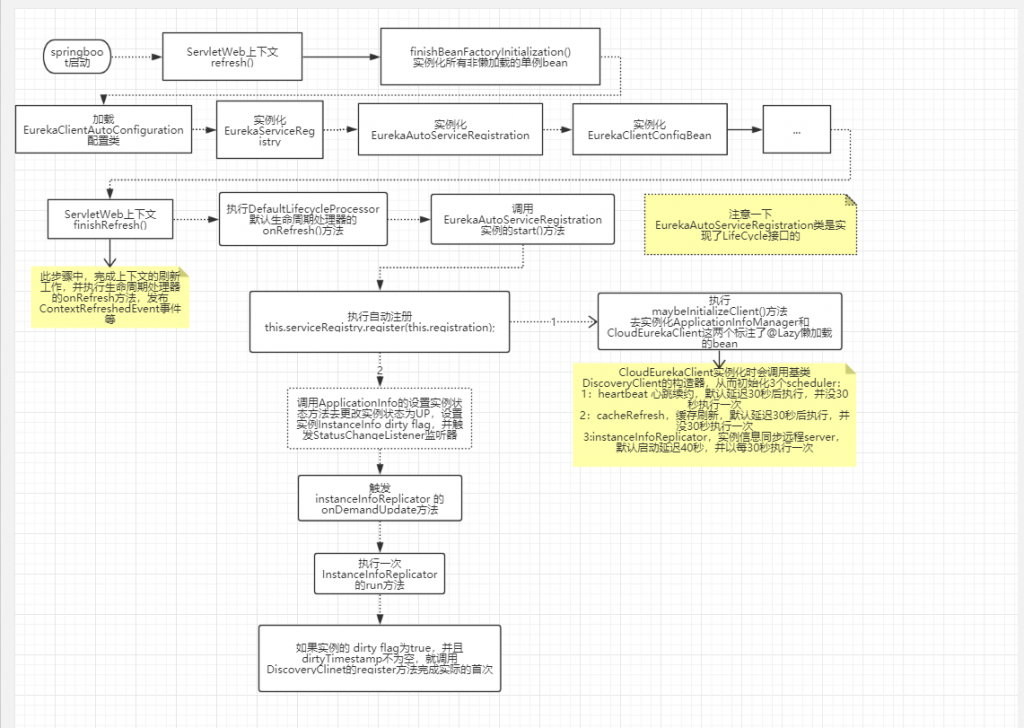
在一个spring cloud项目中,eureka客户端中的关键类DiscoveryClient是怎样实例化的?
首先,需要了解spring boot如何使用spring factories机制加载第三方库,这个可以参考我之前整理的这篇文章:。
以笔者本人使用eureka时所使用的spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client-2.2.2.RELEASE为例,在pom文件中引入该包后,可以IDEA中看到该包下包含了spring.factories
该文件内容如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka.RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.reactive.EurekaReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerEurekaAutoConfiguration org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
我们点EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration,可以看到如下代码:
(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator.class)
(value = "spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled",
matchIfMissing = false)
(proxyBeanMethods = false)
({ EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration.class, // this emulates
// @EnableDiscoveryClient, the import
// selector doesn't run before the
// bootstrap phase
EurekaClientAutoConfiguration.class,
EurekaReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration.class,
ReactiveCommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class })
public class EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration {
}
CloudEurekaClient cloudEurekaClient = new CloudEurekaClient(appManager,
config, this.optionalArgs, this.context);
而CloudEurekaClient类,实际上继承自DiscoveryClient:
public class CloudEurekaClient extends DiscoveryClient {
......
}